Collaboration Kit Flow
Collaboration Kit, formerly known as Collaboration Engine, is a solution for building real-time collaboration features into web applications with a few lines of code. This means that users can work collaboratively — edit and communicate in real time — directly within secure Vaadin web applications.
|
Note
|
License Required for Production
Collaboration Kit follows a runtime billing model, based on the number of users using collaborative features in an application. Developers can start with a free 50-users-per-month license, or request a commercial license with a larger quota of users. Visit the Setting up for production section to learn how to download and install a license.
|
Supported Use Cases
Collaboration Kit supports a few use cases, which are described in the following sub-sections.
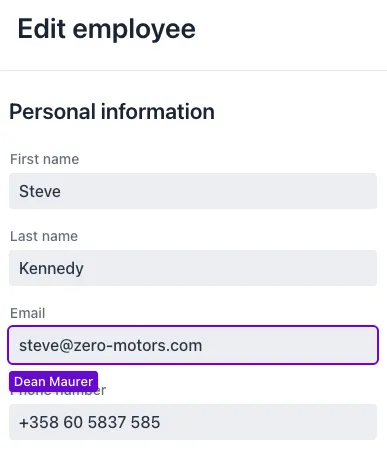
Avatars
Users can see who else is looking at the same data they’re viewing. The avatars are updated when users join or leave.
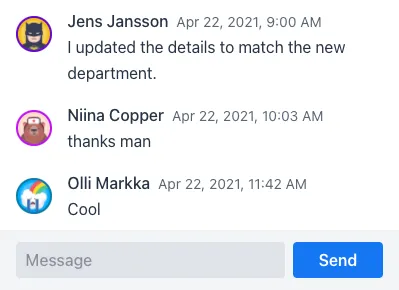
Real-Time Discussion
Users can send messages to each other within the application, either in real time or asynchronously.
How the Kit Works
Collaboration Kit offers an intuitive library that connects to a collaborative backend, the engine.
This backend handles the sharing of data and user-state among application instances in real time. It currently runs in-memory on the application server, although a standalone version that you can deploy within your infrastructure is coming.
Core Concepts
To use Collaboration Kit, to get the most out of it, it’s useful to understand some core concepts. These are covered in the following sub-sections.
Topics
Collaboration between users is managed by collecting data into topic instances that are shared by all users interacting with the same part of the application. A topic is similar to a chat room: it has an identifier that’s unique in the context of the application, and members receive all updates related to any topic in which they’re participating.
Topic identifiers are free-form strings that the developer may choose (e.g., "app" or "contract-126-address"). When building a topic for a work item, it’s a good idea for the name of the entity and the entity’s identifier in the topic identifier. For example, if you’re making a form for editing a Person entity, and the Person has the identifier 120, a good topic name would be "person/120".
Helpers for Specific Use Cases
Collaboration Kit includes several high-level APIs that address the specific use cases of collaboratively editing a form and having real-time discussions.
CollaborationBinder enhances the regular Vaadin Binder to share the current value of each field with all other users configured to use the same topic.
CollaborationAvatarGroup is a component that shows the avatar of every user who is present in a given topic, for example all users currently viewing or editing the same form.
CollaborationMessageList is a component that displays messages submitted with a CollaborationMessageInput component in real time.
Collaboration Managers
Collaboration Managers provides a mid-level API to handle collaborative data for the most common use cases and let developers build their own collaborative logic and custom components:
PresenceManager lets you mark user presence in a Topic and subscribe to presence changes. See Presence Manager documentation for more information.
MessageManager can submit messages to a Topic and subscribe to incoming, new ones. See Message Manager documentation for more information.
FormManager lets you set property values and field highlighting in a form, and to react to changes in them. See Form Manager documentation for more information.
Low-Level API
The low-level Topic API allows synchronizing arbitrary data among users. It’s used internally by Collaboration Managers, but can also be used separately to create custom, collaborative user experiences. The entry point to using the Topic API is by opening a TopicConnection through CollaborationEngine::openTopicConnection.
A topic has multiple named maps and lists which are shared across connections. Each map contains many <String-key, value> pairs, while a list contains ordered values.
It’s strongly recommended that shared values should be immutable instances. Subscribers are notified only when the shared value is replaced with another instance, but not when the content of an existing value is updated.
For complex values in a map, a conditional replace operation is available to prevent overwriting concurrent modifications to other parts of the shared data.
Feature Limitations
Collaboration Kit is production-ready and stable. However, some features are still under development, and are not yet available.
The Kit is currently missing support for complex data structures with nested arrays and maps. You should also be aware that topic data isn’t persisted between server restarts. Applications can manually persist topic data and repopulate after a restart if necessary.
B8534AFE-915D-4680-88E0-957181AB60C8