Chart Styling
Charts can be styled using CSS, and in Flow applications also through the Java API. Vaadin Charts also has many built-in theme variants.
|
Caution
|
Both CSS and Java styling API can’t be used in the same chart
While no error is thrown if different styling methods are used in the same chart, only one method should be used in any chart, since having both could lead to unexpected results.
|
Theme Variants
The following theme variants are available for Charts:
-
Default colors (based on the Lumo or Material theme)
-
Gradient variant with colors varying in hue (
theme="gradient"/ChartVariant.LUMO_GRADIENT/MATERIAL_GRADIENT) -
Monotone variant with colors varying in brightness (
theme="monotone"/ChartVariant.LUMO_MONOTONE/MATERIAL_MONOTONE) -
Classic variant with colors matching those in older versions (
theme="classic"/ChartVariant.LUMO_CLASSIC/MATERIAL_CLASSIC)
See a demo of the variants.
Java Styling API in Flow
The default styling mode in Flow applications uses the Java API. See the Java API reference for details.
CSS Styling
Styling Charts with CSS works similarly to other Vaadin components: create a vaadin-chart.css file in your theme’s components folder, and place the styles there.
It’s also possible to use the @CssImport annotation to load the style sheet in Flow applications.
See Highcharts styling documentation for details on CSS styling of Charts.
CSS Styling Mode for Flow
Flow applications can use CSS styling by enabling "styled mode" in the Chart configuration:
Chart chart = new Chart();
Configuration conf = chart.getConfiguration();
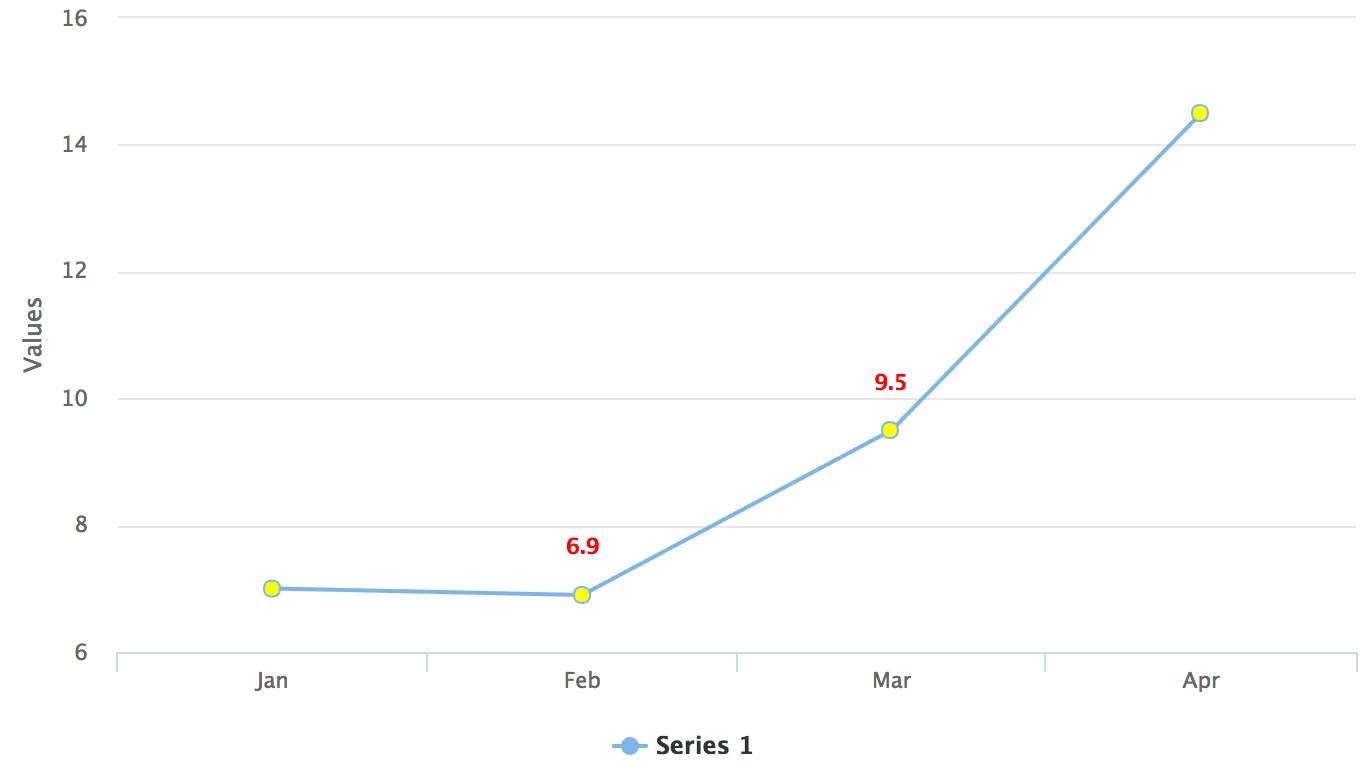
conf.getChart().setStyledMode(true);CSS Styling Example
In this example CSS is used to change the color of point markers to yellow and data labels to red.
:host(.first-chart) g.highcharts-markers > .highcharts-point {
fill: yellow;
}
:host(.first-chart) .highcharts-data-label text {
fill: red;
}@CssImport(value = "./styles/custom-chart-styles.css", themeFor = "vaadin-chart")
public class CssStyleExample extends Div {
public CssStyleExample() {
Chart chart = new Chart();
Configuration configuration = chart.getConfiguration();
configuration.getChart().setType(ChartType.LINE);
configuration.getxAxis().setCategories("Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr");
DataSeries ds = new DataSeries();
ds.setData(7.0, 6.9, 9.5, 14.5);
DataLabels callout = new DataLabels(true);
callout.setShape(Shape.CALLOUT);
callout.setY(-12);
ds.get(1).setDataLabels(callout);
ds.get(2).setDataLabels(callout);
configuration.addSeries(ds);
chart.addClassName("first-chart");
add(chart);
}
}
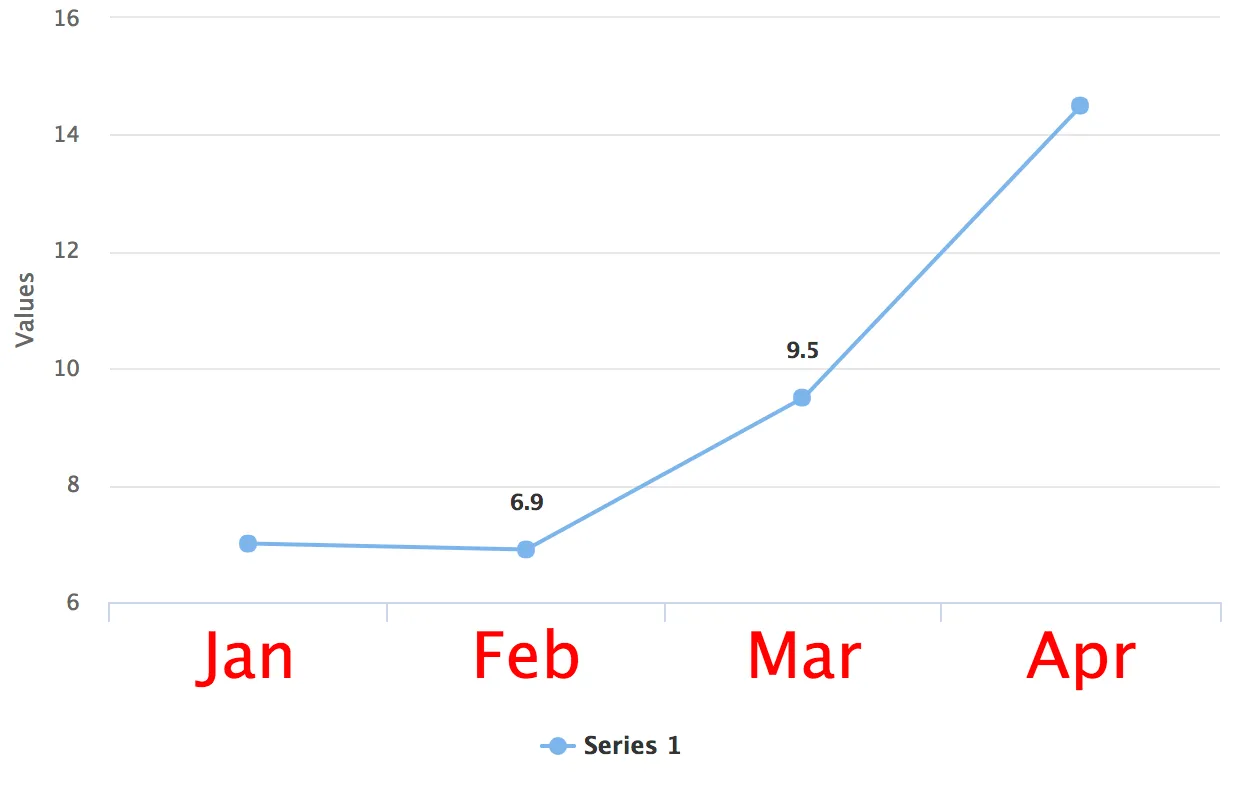
Exposing Chart Elements for Styling (Flow)
CSS class names can be applied both to chart instances and to individual elements in charts.
In the example below, the huge-axis class name is applied to the x-axis of a chart to give it a distinct styling.
@CssImport(value = "./styles/huge-axis.css", themeFor = "vaadin-chart")
public class CssStyleExample extends Div {
public CssStyleExample() {
Chart chart = new Chart();
Configuration configuration = chart.getConfiguration();
DataSeries ds = new DataSeries();
ds.setData(7.0, 6.9, 9.5, 14.5);
configuration.addSeries(ds);
configuration.getxAxis().setCategories("Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr");
// Expose the X-Axis for CSS targeting.
configuration.getxAxis().setClassName("huge-axis");
add(chart);
}
}.huge-axis {
fill: red;
font-size: xx-large;
}
3E5B31FB-DF25-4D1E-80EB-7AB485C7B566
