Running an Application
- Overview
- Eclipse IDE
- IntelliJ IDEA
- NetBeans IDE
Running a Spring Boot Project
If you are developing a Spring Boot project, Spring Boot makes it easier to run a Java web application, because it takes care of starting and configuring the server.
To run your application, all you need to do is to run the Application class that contains the main() method that starts Spring Boot.
IntelliJ automatically detects that you have an Application class with a main() method and displays it in the run configurations drop-down.
To start the application, either:
-
Click the "play" button next to the "run configurations" drop-down.
-
Open
Application.javaand click the "play" button next to the code line containing themain()method.
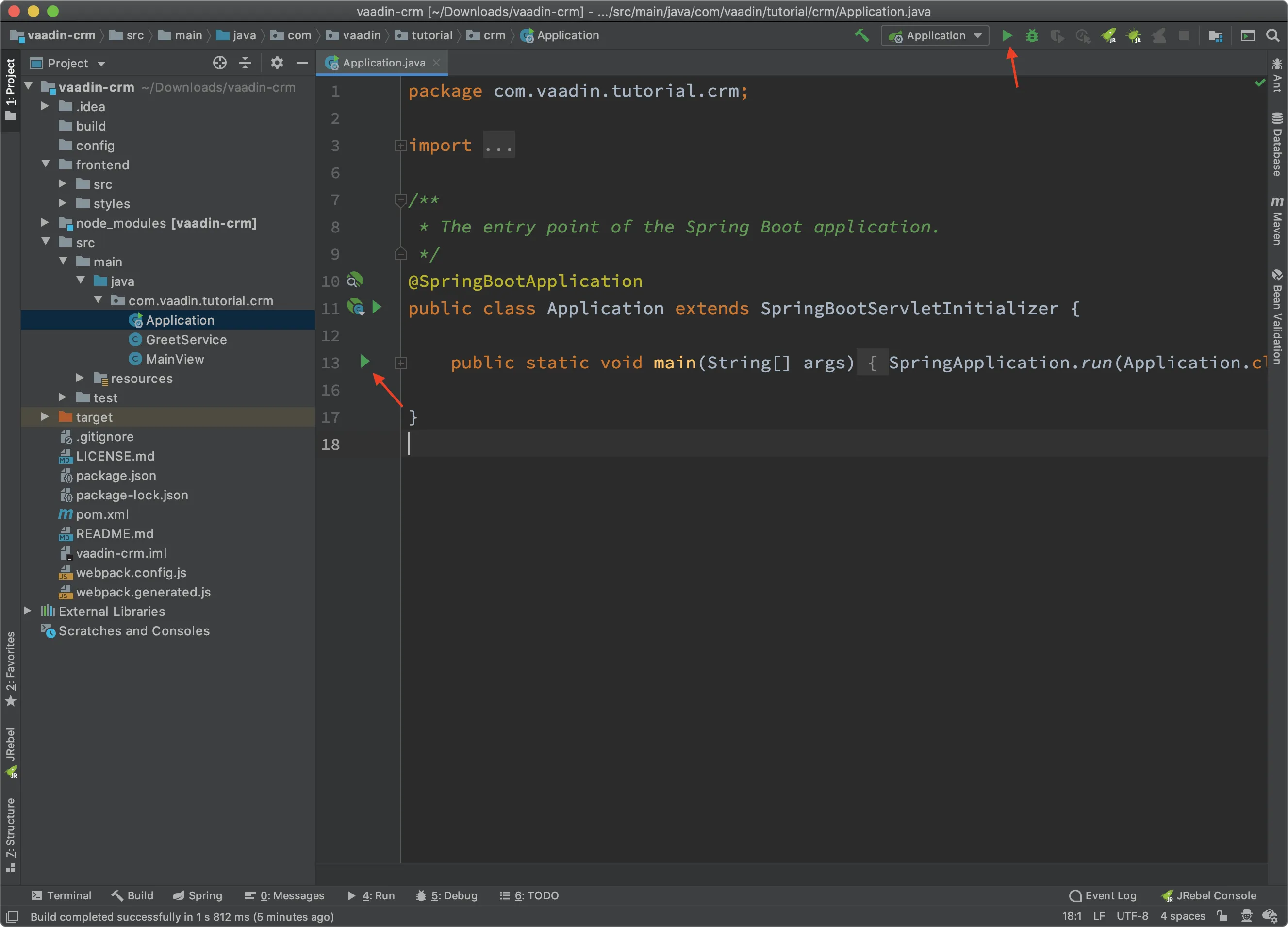
The first time you start a Vaadin application, it downloads front-end dependencies and builds a JavaScript bundle. This can take several minutes, depending on your computer and internet speed.
You know that your application has started when you see the following output in the console:
Source code
Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
Started Application in 80.189 seconds (JVM running for 83.42)You should now be able to open the web application at localhost:8080.
Running Maven Goals
You can use Maven to compile and run a Vaadin application.
IntelliJ IDEA has an excellent integration with Maven.
You can run common commands such as mvn install without having to leave the IDE.
You can run the application in a development server with Maven goals such as jetty:run (plain Java), tomee:run (Java EE and CDI), or spring-boot:run (Spring Boot).
With Spring Boot, you can run the Application class, as described in Running a Spring Boot Project.
-
Open the Maven view by clicking the vertical tab on the right side of the IntelliJ IDEA window:
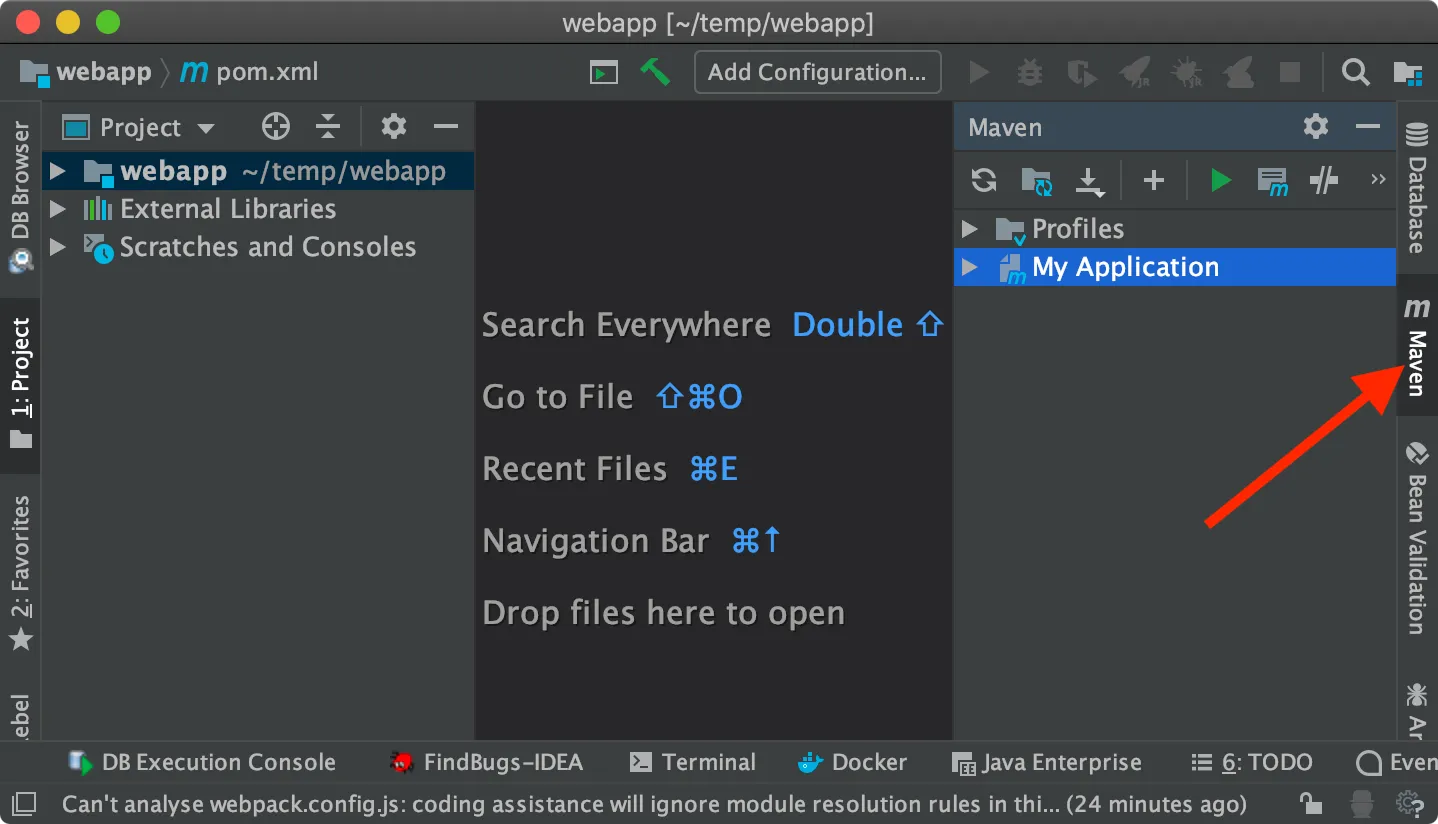 Maven projects view
Maven projects viewThis view shows all the available Maven projects and their build phases and build goals.
-
If you want to run
mvn install, expand the project tree in the Maven view to show the corresponding lifecycle phase.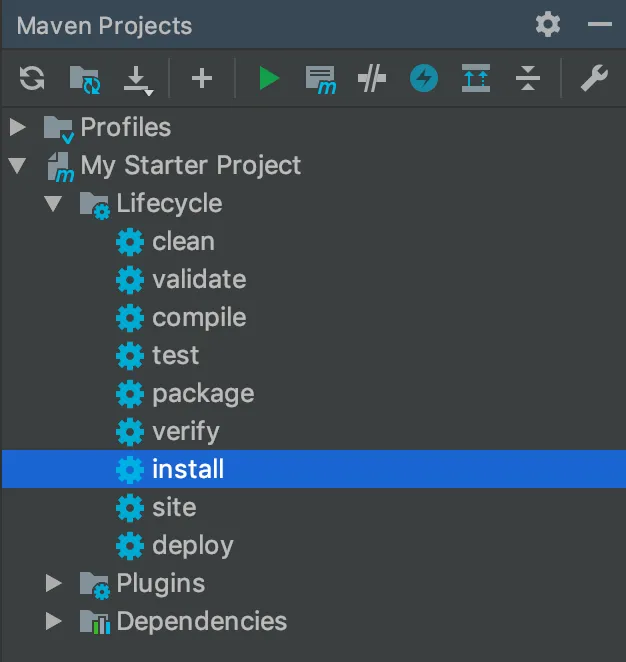
-
Double-click install.
You can see how IntelliJ IDEA executes the install build phase.
First, it executes all the previous phases in Maven’s default lifecycle.
Finally, in the install phase, it downloads dependencies and copies the generated artifacts into your local Maven repository, among other things.
You can use a similar approach to run any Maven goal.
For example, you can double-click the jetty:run goal in the Plugins sub-tree to deploy and run the web application implemented in the project you imported.
Similarly, if you are using Spring Boot, you can double-click spring-boot:run to run the application.
To learn more about the topics covered here:
-
The key concepts in Maven, see Learning Maven Concepts.
Creating a Running Configuration
Since using a goal to run the application could be a frequent task during the development, you may want to create a running configuration for it.
A running configuration is a shortcut to run a specific task from within the IDE.
In the following, you create a running configuration for the jetty:run Maven goal to make it simpler to run the web application.
-
Open the Maven view.
-
Right-click the
jetty:run,tomee:run, orspring-boot:runitem under the appropriate folder.Technology Stack Embedded Server Goal to Run Spring Boot
–
spring-boot:runCDI / Java EE
Apache TomEE
tomee:runPlain Java
Jetty
jetty:run -
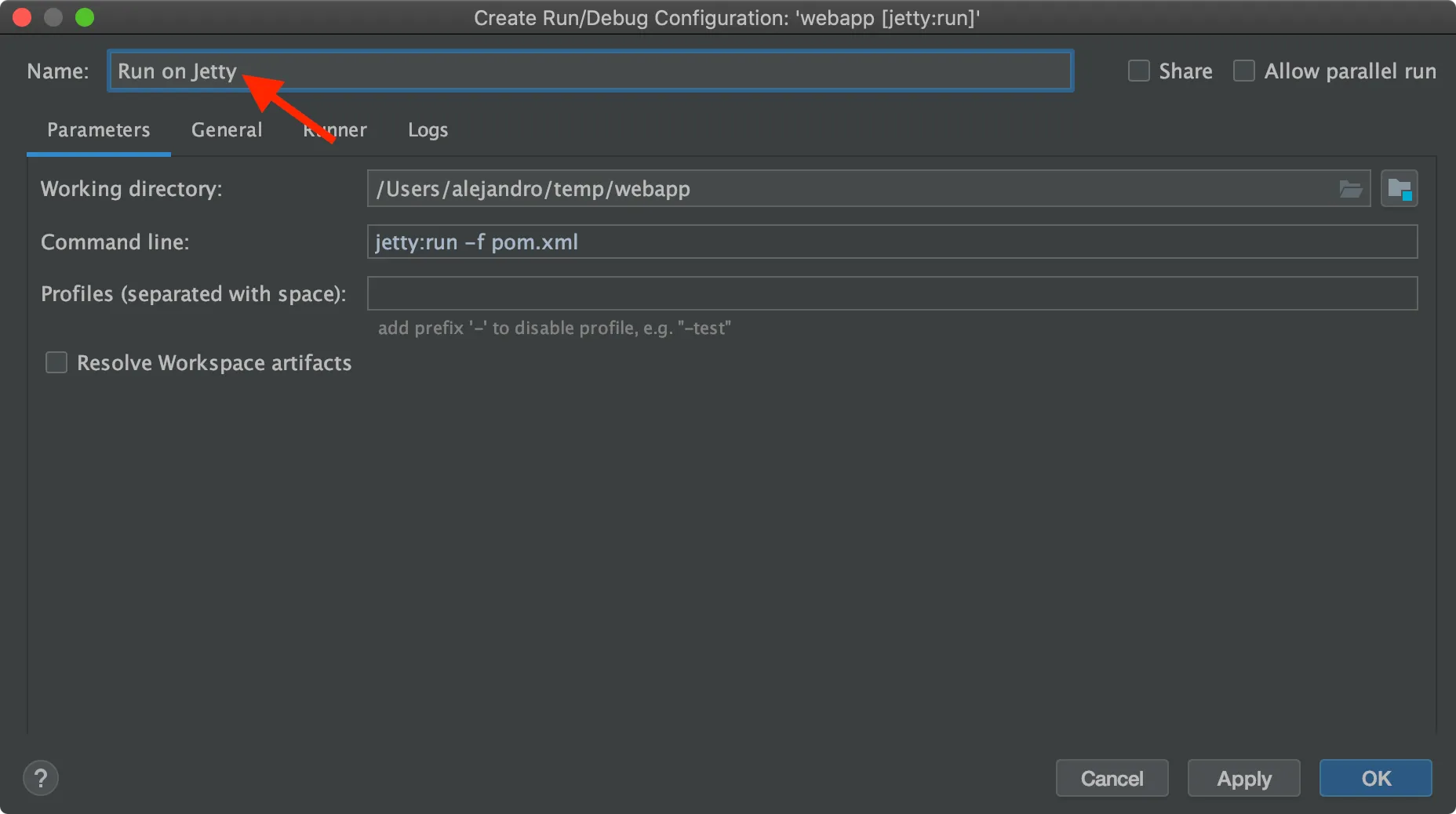
Select Create
webapp [jetty:run](ortomee:runorspring-boot:run):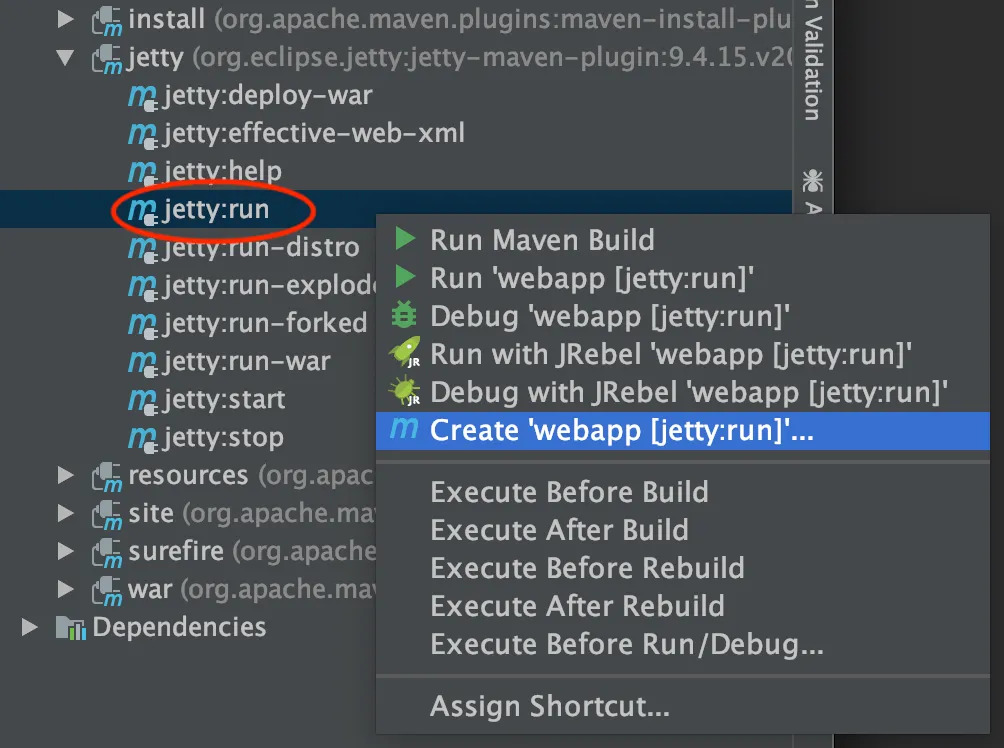
-
For simplicity, change the name of the configuration to Run on Jetty (or TomEE or Spring Boot)
-
Click :
You should see the new option in the top-right corner of IntelliJ IDEA:
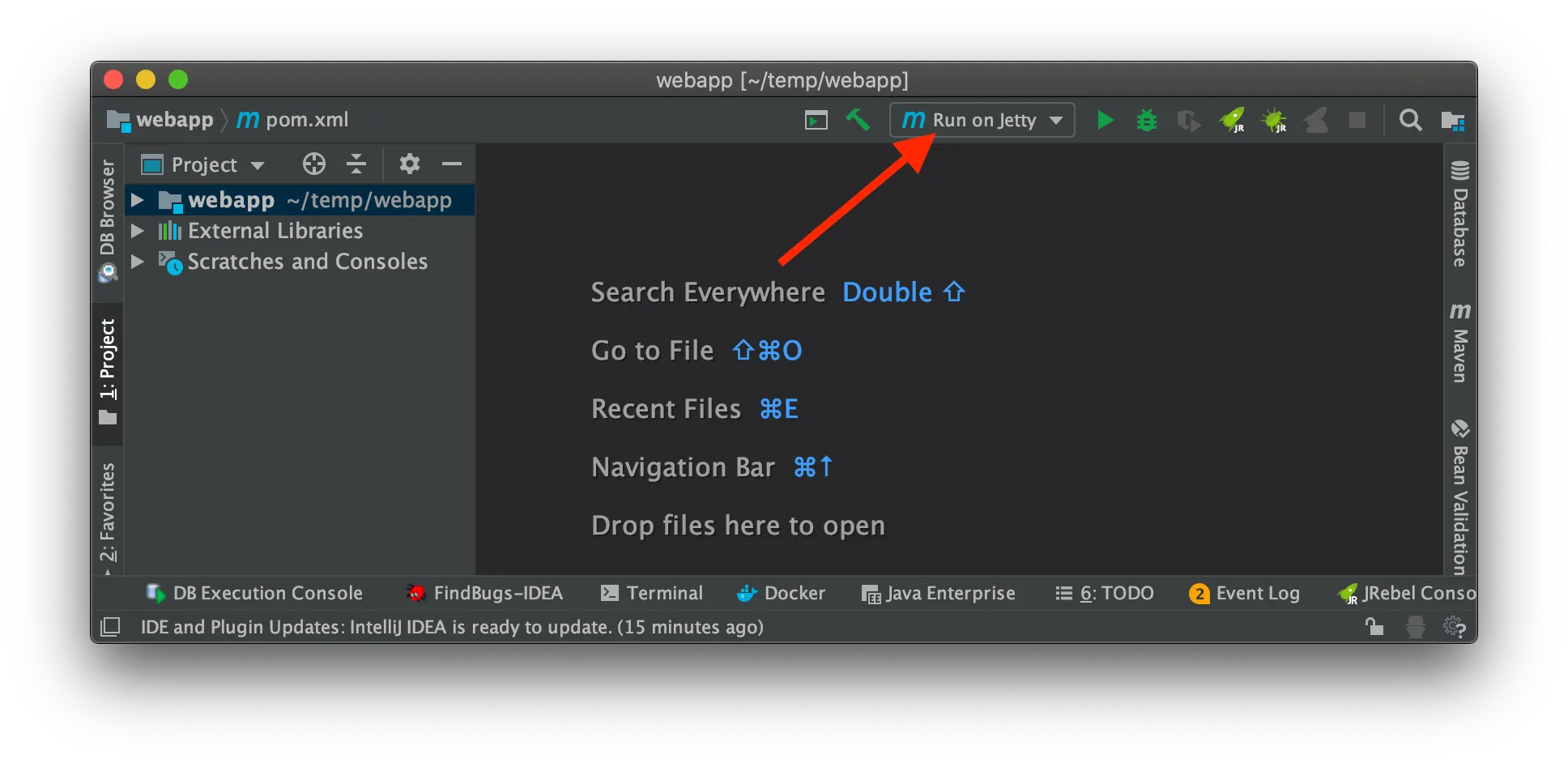
Now you can deploy and run the web application by clicking the "run" (or "debug") icon in the toolbar:
Redeploying during Development
If you edit and save any of the source files, they are compiled automatically, but you can only see the changes by restarting the server. In the Run panel, click the "rerun" icon, or press Ctrl+5 in the editor. You can then refresh the page to use the updated version.
You can also enable Live Reload to have the page refreshed automatically.
F50A0AD3-9989-41D6-8EC5-6F7C698B8062