Vaadin Spring Scopes
Contexts and Scopes in Spring
-
Contexts in Spring are services that manage the lifecycle of objects and handle their injection. A context refers to a situation in which an instance is used with a unique identity. These objects are essentially "singletons" in the context.
-
Scopes are narrower than contexts. While conventional singletons are application-wide, objects managed by a Spring container are "singletons" in a narrower scope. Examples include a user session, a particular UI instance associated with the session, or even a single request. A scope defines the lifecycle of the object, that is, its creation, use, and destruction.
Read more about beans and scopes in Spring.
Using Scopes with Vaadin and Spring
In most programming languages, a variable name refers to a unique object within the scope of the variable. In Spring, an object has a unique identity within a scope but, instead of identifying the object by its variable name, it’s identified by its type (object class) and qualifiers, if any.
With Spring Boot, you need to mark your Vaadin-related bean classes with the @Component annotation to allow them to be picked up as managed beans.
Because there is also a Component class in Vaadin, you can use the @SpringComponent annotation from the Vaadin Spring add-on to avoid having to use fully qualified names.
If no scope is specified in addition to the @SpringComponent / @Component annotation, the component is in singleton scope.
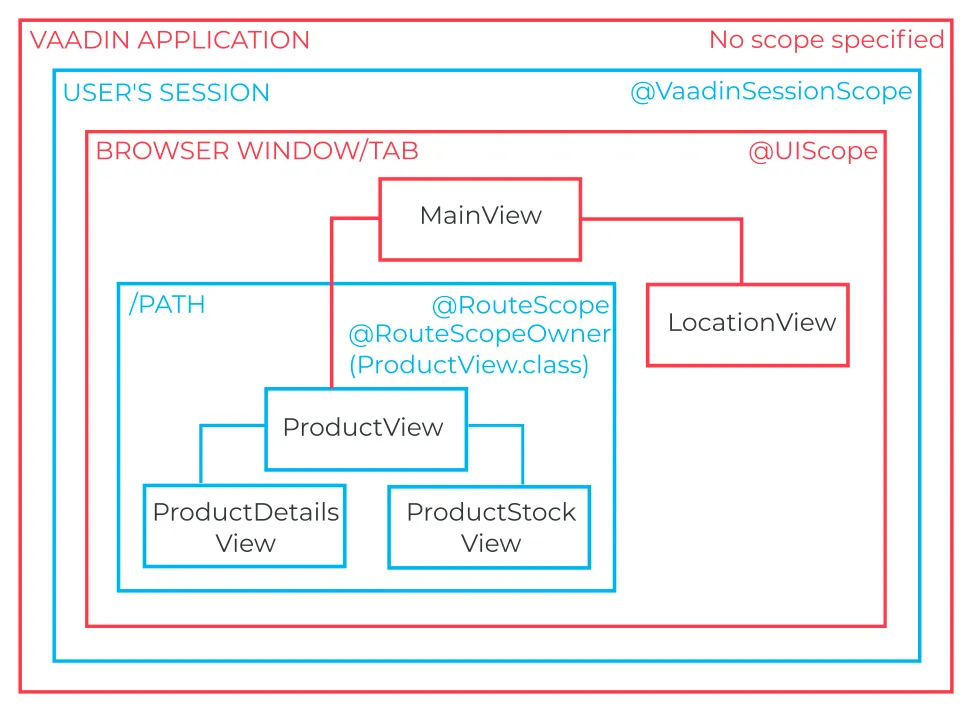
In addition to standard Spring scopes, the Vaadin Spring add-on introduces three additional scopes:
-
VaadinSessionScopeto target beans to a user’s session -
UIScopeto target beans to a browser window or tab opened by the user -
RouteScopeto target beans to certain routing components pointed to by theRouteScopeOwnerqualifier
|
Important
|
Routing components are Spring-initialized beans
All Flow routing components (@Route, RouterLayout or HasErrorParameter) are initialized by Spring, even without explicitly adding the @SpringComponent annotation.
Without any annotations, the components act like a bean in prototype scope.
You can inject other beans to the components, but while @PostConstruct methods work, @PreDestroy methods don’t.
When you want to use another scope for the components, you need to remember to add the @SpringComponent annotation to get the scope applied.
|
|
Note
|
Changes in scopes need server restart
When changing the scope annotations, the application server needs to be restarted to apply the new scopes.
Restart is required even when live reload is enabled.
|
VaadinSessionScope
The @VaadinSessionScope annotation maps the Spring beans to the Vaadin session lifecycle.
It ensures that the same bean instance is used during the whole Vaadin session.
Example: using the @VaadinSessionScope annotation
Source code
Java
@Route("")
public class MainLayout extends Div {
public MainLayout(@Autowired SessionService bean) {
setText(bean.getText());
}
}
@Route("editor")
public class Editor extends Div {
public Editor(@Autowired SessionService bean) {
setText(bean.getText());
}
}
@SpringComponent
@VaadinSessionScope
public class SessionService {
private String uid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
public String getText(){
return "session " + uid;
}
}-
Provided you access the application from the same Vaadin session, the same instance of
SessionServiceis used. This is because it’s session-scoped. -
If you open the root target in one browser tab, and the
editortarget in another, the text in both is the same. This happens because the session is the same, even though the tabs (andUIinstances) are different.
See Application Lifecycle > User Session for more information on session handling.
UIScope
The @UIScope annotation manages the Spring beans during the UI lifecycle.
Example: using the @UIScope annotation.
Source code
Java
@Route("")
public class MainLayout extends Div {
public MainLayout(@Autowired UIService bean) {
add(new Span(bean.getText()));
add(new RouterLink("Open editor", Editor.class));
}
}
@Route("editor")
public class Editor extends Div {
public Editor(@Autowired UIService bean) {
add(new Span(bean.getText()));
add(new RouterLink("Open MainLayout", MainLayout.class));
}
}
@SpringComponent
@UIScope
public class UIService {
private String uid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
public String getText() {
return "ui " + uid;
}
}-
The
UIServicebean instance is the same inside the sameUI. -
If you open the
MainLayoutview in one browser tab or window, and theEditorview in another, the text in each is different, because theUIinstances are different. -
When navigating inside the same browser tab between the
MainLayoutandEditor, the text stays the same, since the service is the same.
See Application Lifecycle > Loading a UI for more information on UIs.
|
Note
|
Preserving UIScope beans
Unlike with earlier Vaadin versions 7 and 8, the UI and thus the UIScope beans aren’t preserved when the @PreserveOnRefresh annotation is used and the browser is refreshed.
To preserve the beans on refresh, you need to use @RouteScope instead (available since V21), as described in the next chapter.
|
RouteScope and RouteScopeOwner
The @RouteScope annotation ties the beans to the lifecycle of Vaadin Flow routing components (@Route, RouterLayout, HasErrorParameter).
Since there can be multiple nested levels of routing components present at once, an additional @RouteScopeOwner qualifier annotation can be used to specify the owner routing component.
Without the owner qualifier, the owner is the currently active routing component at the time of injection.
As long as the owner routing component is part of the active view chain, all beans owned by it remain in the scope.
Any routing component can be a @RouteScope bean itself, and the owner can be any parent RouterLayout in the route chain hierarchy.
See Defining Routes With @Route and Router Layouts and Nested Router Targets for more about route targets, route layouts, and the active route chain.
Example: sharing a bean between two child views with the same parent layout
Source code
Java
@SpringComponent
@RouteScope
@RouteScopeOwner(ParentView.class)
public class RouteService {
private String uid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
public String getText() {
return "ui " + uid;
}
}
@Route("")
@RoutePrefix("parent")
public class ParentView extends VerticalLayout
implements RouterLayout {
public ParentView(
@Autowired @RouteScopeOwner(ParentView.class)
RouteService routeService) {
add(new Span("Parent view:" + routeService.getText()),
new RouterLink("Open Child-A", ChildAView.class),
new RouterLink("Open Child-B", ChildBView.class),
new RouterLink("Open Sibling", SiblingView.class));
}
}
@Route(value = "child-a", layout = ParentView.class)
public class ChildAView extends VerticalLayout {
public ChildAView(
@Autowired @RouteScopeOwner(ParentView.class)
RouteService routeService) {
add(new Text("Child-a: " + routeService.getText()));
}
}
@Route(value = "child-b", layout = ParentView.class)
public class ChildBView extends VerticalLayout {
public ChildBView(
@Autowired @RouteScopeOwner(ParentView.class)
RouteService routeService) {
add(new Text("Child-a: " + routeService.getText()));
}
}
@Route(value = "sibling")
public class SiblingView extends VerticalLayout {
public SiblingView() {
add(new RouterLink("Open ParentView", ParentView.class),
new RouterLink("Open Child-A", ChildAView.class),
new RouterLink("Open Child-B", ChildBView.class));
}
}-
The injected
RouteServicebean instance is the same while theParentViewis attached, such as when navigating between the child views. -
When navigating to the
SiblingView, theParentViewis detached. When navigating back to theParentView(or child views), a newRouteServicebean is created.
|
Caution
|
Injecting to wider scope
Injecting a "narrower" RouteScope bean into "wider" scope, like parent layout’s RouteScope or UIScope, can cause problems.
For example, if you store a RouteScope bean into a UIScope bean, the bean might become stale after navigation.
|
The @RouteScopeOwner qualifier has to be placed both on top of the bean class and on the injection point of the bean.
The annotation can be omitted in the injection point when the bean implementation can be resolved unambiguously by Spring (as it could be in the previous example).
However, it’s recommended to have it there for better code readability.
Having an owner view class as a value in the @RouteScopeOwner for a model/business logic bean class ties the application’s view layer to a model/business layer.
It can be decoupled, for example, by splitting the bean class into an interface and its implementation class, and then using the interface in the view class and marking the concrete bean implementation class with @RouteScopeOwner.
@RouteScope without @RouteScopeOwner to Replace @ViewScope from Vaadin 7 / 8
When the @RouteScopeOwner annotation is omitted, the owner is the currently active route target.
In nested routing hierarchies, the owner is the "leaf" / "bottom-most" routing component, that is, navigation target.
The bean remains in scope for as long as the navigation target stays active (attached to the UI).
Compared to a @Scope("prototype") bean injected to the routing component, the @RouteScope bean without an owner has its @PreDestroy method called when the routing component is no longer active.
Using @RouteScope without specifying an owner is a replacement for the @ViewScope from Vaadin 7 or 8.
|
Note
|
Model-View-Presenter
The following example is based on the model-view-presenter design pattern, for the sake of demonstration. It isn’t a best-practice example.
It allows splitting different logical parts of the application, but adds a lot of boilerplate code.
|
Example: @RouteScope without owner behaves like the legacy Vaadin @ViewScope
Source code
Java
/*
* Presenter responsible for application logic and setting data for the view.
*/
@SpringComponent
@RouteScope
public class UserProfilePresenter {
private final UserService service;
private final UserModel model;
@Autowired
public UserProfilePresenter(UserService service, UserModel model) {
this.service = service;
}
public void init(UserProfileView view) {
Integer id = model.getActiveUserId();
if (id != null) {
view.showUser(service.getUser(id));
} else {
view.redirectToLogin();
}
}
}
@Route("user-profile")
public class UserProfileView extends VerticalLayout {
private final UserProfilePresenter presenter;
public UserProfileView(@Autowired UserProfilePresenter presenter) {
this.presenter = presenter;
}
@PostConstruct
private void init() {
presenter.init(this);
}
public void showUser(User user) {
removeAll();
add(new Div(new Text("Hello " + user.getName())));
}
public void redirectToLogin() {
Notification.show("Not logged in!");
UI.getCurrent().navigate("login");
}
}
@SpringComponent
@VaadinSessionScope
// A bean storing the active user for the session
public class UserModel {
private Integer activeUserId;
// getter and setter omitted
}
@Service
// Service for fetching the user entity from backend
public class UserService {
public User getUser(Integer id) {
// implementation omitted
}
}
// User entity
public class User {
private String name;
// getter and setter omitted
}-
In this example, a new
UserProfilePresenterbean is created every time theUserProfileViewview is opened. -
The presenter bean stays the same during the time the view is attached to the UI.
Preserving Beans during Browser Refresh
By default, when the user refreshes the page, all routing components are recreated.
This applies to @UIScope and @RouteScope beans too; new bean instances are created and injected to the new routing components.
It’s possible to tell the framework to preserve the routing components during refresh with the @PreserveOnRefresh annotation (see here for more information).
When the @PreserveOnRefresh annotation is used on a routing component that has @RouteScope beans injected to it, the beans are preserved too.
Example: preserving beans with @RouteScopeOwner targeting a component with @PreserveOnRefresh
Source code
Java
@SpringComponent
@RouteScope
@RouteScopeOwner(MainLayout.class)
public class PreservedBean {
private String uid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
public String getText() {
return uid;
}
}
@Route("") // optional, could use a subview with @Route instead
@PreserveOnRefresh
public class MainLayout extends VerticalLayout
implements RouterLayout {
public MainLayout(
@Autowired @RouteScopeOwner(ParentView.class)
PreservedBean bean) {
add(new Span("UID:" + bean.getText()));
}
}-
In this example, both the
MainLayoutcomponent and thePreservedBeaninjected bean are preserved after browser refresh. The text stays the same. -
If the
@PreserveOnRefreshannotation is removed from the layout, both the component and the bean are recreated after browser refresh. The text would change.
Beans in UIScope Aren’t Preserved
Injected beans aren’t preserved when they are in UIScope, but only in RouteScope, regardless of whether @PreserveOnRefresh is used.
However, any currently active routing components are preserved, even if they are in UIScope.
This is due to the nature of the @PreserveOnRefresh feature implementation.
The UI instance itself isn’t preserved, but routing components are.
Any bean tied to the UI instance with UIScope is recreated, and the preserved routing components are moved to the new UI.
To preserve beans during a browser refresh, you need to use @RouteScope, as shown earlier.
23B703EE-D5C7-44CE-971A-A64EE4D89B7D