Vaadin Framework
Vaadin Framework is a Java web application development framework that is designed to make creation and maintenance of high quality web-based user interfaces easy. Vaadin supports two different programming models: server-side and client-side. The server-driven programming model is the more powerful one. It lets you forget the web and program user interfaces much like you would program a desktop application with conventional Java toolkits such as AWT, Swing, or SWT. But easier.
While traditional web programming is a fun way to spend your time learning new web technologies, you probably want to be productive and concentrate on the application logic. The server-side Vaadin framework takes care of managing the user interface in the browser and the AJAX communications between the browser and the server. With the Vaadin approach, you do not need to learn and deal directly with browser technologies, such as HTML or JavaScript.
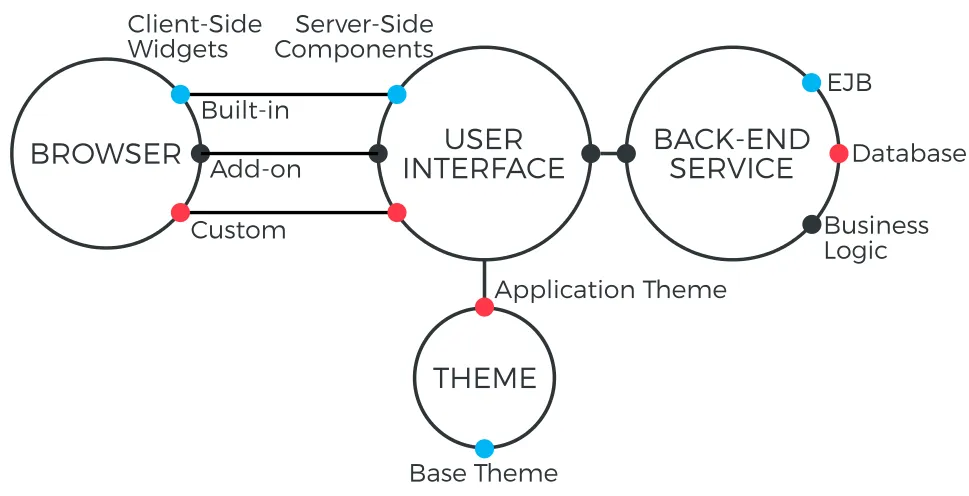
Vaadin application architecture illustrates the basic architectures of web applications made with Vaadin. The server-side application architecture consists of the server-side framework and a client-side engine. The engine runs in the browser as JavaScript code, rendering the user interface, and delivering user interaction to the server. The UI logic of an application runs as a Java Servlet in a Java application server.
As the client-side engine is executed as JavaScript in the browser, no browser plugins are needed for using applications made with Vaadin. This gives it an edge over frameworks based on Flash, Java Applets, or other plugins. Vaadin relies on the support of Google Web Toolkit for a wide range of browsers, so that the developer does not need to worry about browser support.
Because HTML, JavaScript, and other browser technologies are essentially invisible to the application logic, you can think of the web browser as only a thin client platform. A thin client displays the user interface and communicates user events to the server at a low level. The control logic of the user interface runs on a Java-based web server, together with your business logic. By contrast, a normal client-server architecture with a dedicated client application would include a lot of application specific communications between the client and the server. Essentially removing the user interface tier from the application architecture makes our approach a very effective one.
Behind the server-driven development model, Vaadin makes the best use of AJAX ( Asynchronous JavaScript and XML, see "AJAX" for a description) techniques that make it possible to create Rich Internet Applications (RIA) that are as responsive and interactive as desktop applications.
In addition to the server-side Java application development, you can develop on the client-side by making new widgets in Java, and even pure client-side applications that run solely in the browser. The Vaadin client-side framework includes Google Web Toolkit (GWT), which provides a compiler from Java to the JavaScript that runs in the browser, as well a full-featured user interface framework. With this approach, Vaadin is pure Java on both sides.
Vaadin uses a client-side engine for rendering the user interface of a server-side application in the browser. All the client-server communications are hidden well under the hood. Vaadin is designed to be extensible, and you can indeed use any 3rd-party widgets easily, in addition to the component repertoire offered in Vaadin. In fact, you can find hundreds of add-ons in the Vaadin Directory.
Vaadin allows flexible separation between the appearance, structure, and interaction logic of the user interface. You can design the layouts either programmatically or declaratively, at the level of your choosing. The final appearance is defined in themes in CSS or Sass, as described in "Themes".
We hope that this is enough about the basic architecture and features of Vaadin for now. You can read more about it later in "Architecture", or jump straight to more practical things in "Writing a Server-Side Web Application".