Basic Use
- Basic Chart Configuration
- Plot Options
- Chart Data Series
- Axis Configuration
- Displaying Multiple Series
- Mixed Type Charts
The Chart is a regular Vaadin component, which you can add to a
layout. You can give the chart type in the constructor or set it later in the
chart model.
Source code
Java
Chart chart = new Chart(ChartType.COLUMN);
//or
Chart chart = new Chart();
chart.getConfiguration().getChart().setType(ChartType.COLUMN);
...
layout.add(chart);The chart types are described in "Chart Types". The main parts of a chart are illustrated in Chart Elements. Styling a chart is discussed in "CSS Styling"
To actually display something in a chart, you typically need to configure the following aspects:
-
Basic chart configuration
-
Configure plot options for the chart type
-
Configure one or more data series to display
-
Configure axes
The plot options can be configured for each data series individually, or for different chart types in mixed-type charts.
Basic Chart Configuration
After creating a chart, you need to configure it further. At the least, you need to specify the data series to be displayed in the configuration.
Most methods available in the Chart object handle its basic Vaadin
component properties. All the chart-specific properties are in a separate
Configuration object, which you can access with the
getConfiguration() method.
Source code
Java
Configuration conf = chart.getConfiguration();
conf.setTitle("Reindeer Kills by Predators");
conf.setSubTitle("Kills Grouped by Counties");The configuration properties are described in more detail in "Chart Configuration".
Plot Options
Many chart settings can be configured in the plot options of the chart or data series. Some of the options are chart type specific, as described later for each chart type, while many are shared.
For example, for line charts, you could disable the point markers as follows:
Source code
Java
// Disable markers from lines
PlotOptionsLine plotOptions = new PlotOptionsLine();
plotOptions.setMarker(new Marker(false));
conf.setPlotOptions(plotOptions);You can set the plot options for the entire chart or for each data series separately, allowing also mixed-type charts, as described in Mixed Type Charts.
The shared plot options are described in "Plot Options".
Chart Data Series
The data displayed in a chart is stored in the chart configuration as a list of
Series objects. A new data series is added in a chart with the
addSeries() method.
Source code
Java
ListSeries series = new ListSeries("Diameter");
series.setData(4900, 12100, 12800,
6800, 143000, 125000,
51100, 49500);
conf.addSeries(series);The data can be specified with a number of different series types
DataSeries, ListSeries, HeatSeries
and TreeSeries.
Data point features, such as name and data labels, can be defined in the versatile
DataSeries, which contains DataSeriesItem items.
Special chart types, such as box plots and 3D scatter charts require using their
own special data point type.
The data series configuration is described in more detail in "Chart Data".
Axis Configuration
One of the most common tasks for charts is customizing its axes. At the least, you usually want to set the axis titles. Usually you also want to specify labels for data values in the axes.
When an axis is categorical rather than numeric, you can define category labels for the items. They must be in the same order and the same number as you have values in your data series.
Source code
Java
XAxis xaxis = new XAxis();
xaxis.setCategories("Mercury", "Venus", "Earth",
"Mars", "Jupiter", "Saturn",
"Uranus", "Neptune");
xaxis.setTitle("Planet");
conf.addxAxis(xaxis);Formatting of numeric labels can be done with JavaScript expressions, for example as follows:
Source code
Java
// Set the Y axis title
YAxis yaxis = new YAxis();
yaxis.setTitle("Diameter");
yaxis.getLabels().setFormatter(
"function() {return Math.floor(this.value/1000) + \'Mm\';}");
yaxis.getLabels().setStep(2);
conf.addyAxis(yaxis);Displaying Multiple Series
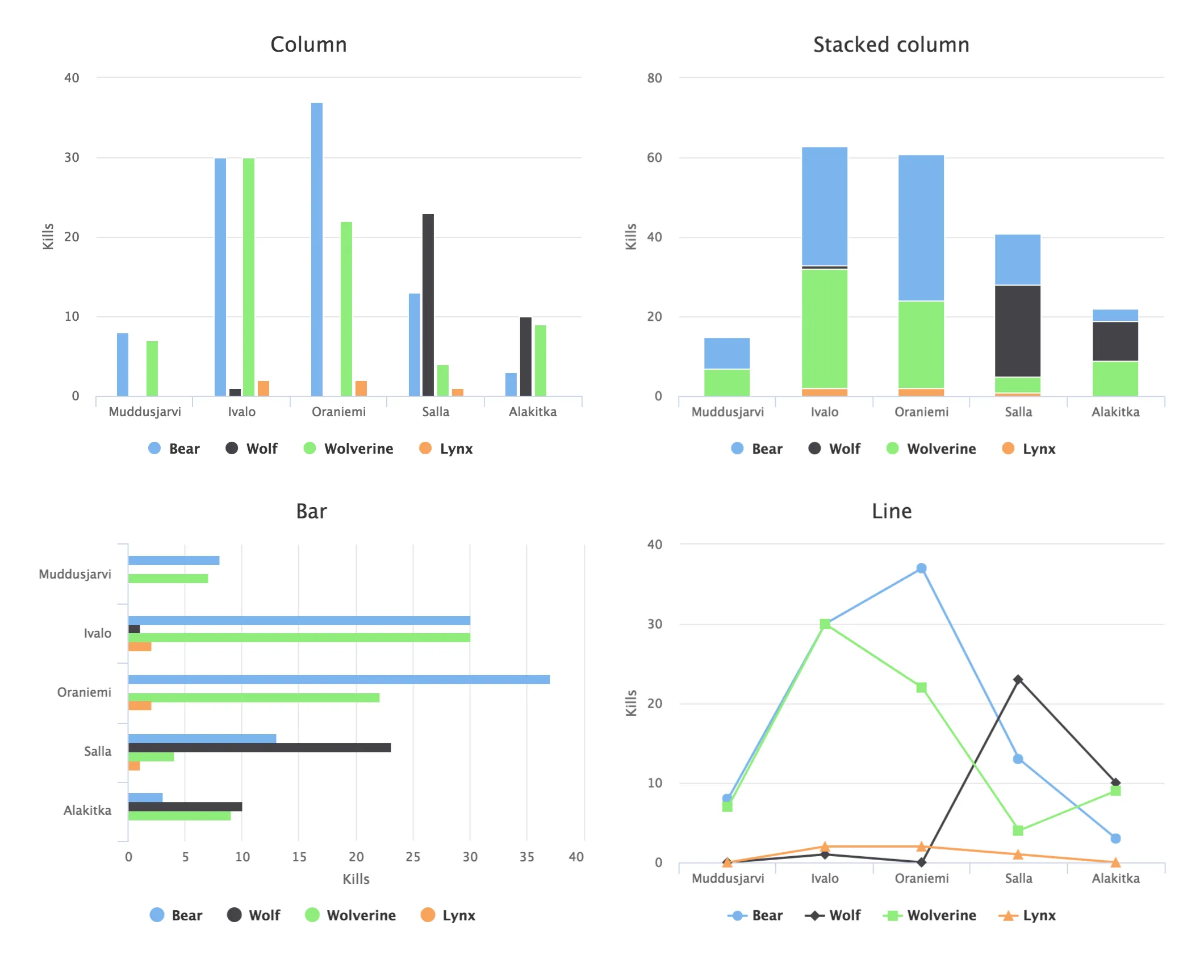
The simplest data, which we saw in the examples earlier in this chapter, is one-dimensional and can be represented with a single data series. Most chart types support multiple data series, which are used for representing two-dimensional data. For example, in line charts, you can have multiple lines and in column charts the columns for different series are grouped by category. Different chart types can offer alternative display modes, such as stacked columns. The legend displays the symbols for each series.
Source code
Java
// The data
// Source: V. Maijala, H. Norberg, J. Kumpula, M. Nieminen
// Calf production and mortality in the Finnish
// reindeer herding area. 2002.
String predators[] = {"Bear", "Wolf", "Wolverine", "Lynx"};
int kills[][] = { // Location:
{8, 0, 7, 0}, // Muddusjarvi
{30, 1, 30, 2}, // Ivalo
{37, 0, 22, 2}, // Oraniemi
{13, 23, 4, 1}, // Salla
{3, 10, 9, 0}, // Alakitka
};
// Create a data series for each numeric column in the table
for (int predator = 0; predator < 4; predator++) {
ListSeries series = new ListSeries();
series.setName(predators[predator]);
// The rows of the table
for (int location = 0; location < kills.length; location++)
series.addData(kills[location][predator]);
conf.addSeries(series);
}The result for both regular and stacked column chart is shown in
Multiple Series in a Chart. Stacking is enabled with
setStacking() in PlotOptionsColumn.
Mixed Type Charts
You can enable mixed charts by setting the chart type in the
PlotOptions object for a data series, which overrides the default
chart type set in the Chart object. You can also control the animation and
other settings for the series in the plot options.
For example, to get a line chart, you need to use PlotOptionsLine.
Source code
Java
// A data series as column graph
DataSeries series1 = new DataSeries();
PlotOptionsColumn options1 = new PlotOptionsColumn();
series1.setPlotOptions(options1);
series1.setData(4900, 12100, 12800,
6800, 143000, 125000, 51100, 49500);
conf.addSeries(series1);
// A data series as line graph
ListSeries series2 = new ListSeries("Diameter");
PlotOptionsLine options2 = new PlotOptionsLine();
series2.setPlotOptions(options2);
series2.setData(4900, 12100, 12800,
6800, 143000, 125000, 51100, 49500);
conf.addSeries(series2);In the above case, where we set the chart type for each series, the overall chart type is irrelevant.
|
Note
| Gauge and solid gauge series should not be combined with series of other types. |
|
Note
| A bar series inverts the entire chart, combine with care. |
7016600D-AD8C-4707-89A9-C7208CFC7ED0