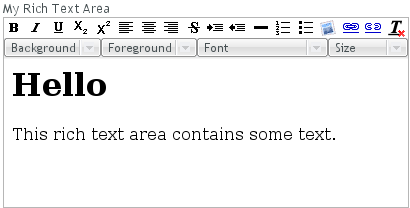
5.9. RichTextArea
The RichTextArea field allows entering or editing
formatted text. The toolbar provides all basic editing functionalities. The
text content of RichTextArea is represented in HTML
format. RichTextArea inherits
TextField and does not add any API functionality over
it. You can add new functionality by extending the client-side components
VRichTextArea and
VRichTextToolbar.
As with TextField, the textual content of the rich text
area is the Property of the field and can be set with
setValue() and read with
getValue().
// Create a rich text area
final RichTextArea rtarea = new RichTextArea();
rtarea.setCaption("My Rich Text Area");
// Set initial content as HTML
rtarea.setValue("<h1>Hello</h1>\n" +
"<p>This rich text area contains some text.</p>");
Above, we used context-specific tags such as <h1> in
the initial HTML content. The rich text area component does not allow creating
such tags, only formatting tags, but it does preserve them unless the user
edits them away. Any non-visible whitespace such as the new line character
(\n) are removed from the content. For example, the value
set above will be as follows when read from the field with
getValue():
<h1>Hello</h1> <p>This rich text area contains some text.</p>
The rich text area is one of the few components in Vaadin that contain textual
labels. The selection boxes in the toolbar are in English and currently can
not be localized in any other way than by inheriting or reimplementing the
client-side VRichTextToolbar widget. The buttons can be
localized simply with CSS by downloading a copy of the toolbar background
image, editing it, and replacing the default toolbar. The toolbar is a single
image file from which the individual button icons are picked, so the order of
the icons is different from the rendered. The image file depends on the
client-side implementation of the toolbar.
.v-richtextarea-richtextexample .gwt-ToggleButton
.gwt-Image {
background-image: url(img/richtextarea-toolbar-fi.png)
!important;
}
The user input from a RichTextArea is transmitted
as XHTML from the browser to server-side and is not sanitized. As the
entire purpose of the RichTextArea component is to
allow input of formatted text, you can not sanitize it just by removing
all HTML tags. Also many attributes, such as style,
should pass through the sanitization.
See Section 12.9.1, “Sanitizing User Input to Prevent Cross-Site Scripting” for more details on Cross-Site scripting vulnerabilities and sanitization of user input.
.v-richtextarea { }
.v-richtextarea .gwt-RichTextToolbar { }
.v-richtextarea .gwt-RichTextArea { }
The rich text area consists of two main parts: the toolbar with overall
style .gwt-RichTextToolbar and the editor area with
style .gwt-RichTextArea. The editor area obviously
contains all the elements and their styles that the HTML content
contains. The toolbar contains buttons and drop-down list boxes with the
following respective style names:
.gwt-ToggleButton { }
.gwt-ListBox { }